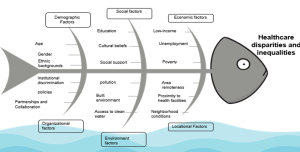
SLIDE 7 : A Fishbone Diagram for Health Inequalities and Disparities
SLIDE 8 : Evidence-based Recommendations for Addressing Health Disparities and Inequalities
Medicaid expansion
Radley et al. (2021) argue that over 30 million Americans are still uninsured, especially people of color. Income and economic status contribute to disparities in access to Medicaid insurance covers. Therefore, expanding Medicaid by revising eligibility criteria can eliminate inequalities in care affordability and address the problem of uninsured and underinsured Americans.
Developing Community-based programs and policies for ensuring health equality
Localized interventions and programs can intercept and improve social determinants of health, including education, housing, built environment, healthcare justice, and literacy (Gomez et al., 2020).
The national and state governments should collaborate to attend to the root-causes of health disparities by implementing community-based interventions.
SLIDE 9 : Evidence-based Recommendations Cont’d
Eliminating organizational issues that result in health disparities
Healthcare organizations in the US are responsible for care coordination, patient safety, and patient-centered care.
Various institutional issues compromise the internal capacity to uphold these objectives.
Lavizzo-Mourey et al. (2021) argue that racial and ethnic disparities in healthcare organizations exist and are disproportionate to minority groups such as Black Americans and Asian Americans.
It is essential to address institutional incivility by developing policies and ethical standards, enhancing multidisciplinary collaboration, and eliminating workplace stressors.
SLIDE 10 : Evidence-based Recommendations Cont’d
Equal and fair distribution of socio-economic resources
As noted earlier, social determinants of health such as income status, poverty, education, work conditions, housing, and health literacy influence how people access, experience, and receive healthcare services.
Disparities that emanate from these factors prompt governments to ensure equal and fair distribution of socio-economic resources to improve situations and eliminate inequalities (Gomez et al., 2021).
It is essential to conceptualize policies and measures for ensuring maximum resource utilization at the community and institutional levels to address health disparities.
Conclusion
Health disparities pose a challenge to the current healthcare systems due to their relationship with the social determinants of health (SDOH)
Therefore, addressing the prevailing inequalities requires practical analysis tools and plan frameworks.
Examples of evidence-based recommendations for addressing health disparities include;
Medicaid expansion
Equal and fair distribution of socio-economic resources
Developing community-based programs and policies for ensuring health equality
Eliminating structural racism and other issues in healthcare organizations.
References
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. (2021). National healthcare quality and disparities report (pp. 1-316). AHRQ. https://www.ahrq.gov/sites/default/files/wysiwyg/research/findings/nhqrdr/2021qdr.pdf
Gómez, C., Kleinman, D., Pronk, N., Wrenn Gordon, G., Ochiai, E., & Blakey, C. et al. (2021). Addressing health equity and social determinants of health through healthy people 2030. Journal of Public Health Management and Practice, s249-s257. https://doi.org/10.1097/phh.0000000000001297
Islam, M. (2019). Social Determinants of Health and Related Inequalities: Confusion and Implications. Frontiers In Public Health, 7, 1-4. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2019.00011